If you’re still using AI as a tool, you’re behind. The future is agent-based systems.
Tool usage = linear productivity gain
Agent usage = exponential automation gain
If you:
Use ChatGPT to write code → +30% speed
Use agents to build, test, deploy, review → 3x output
That’s the shift.
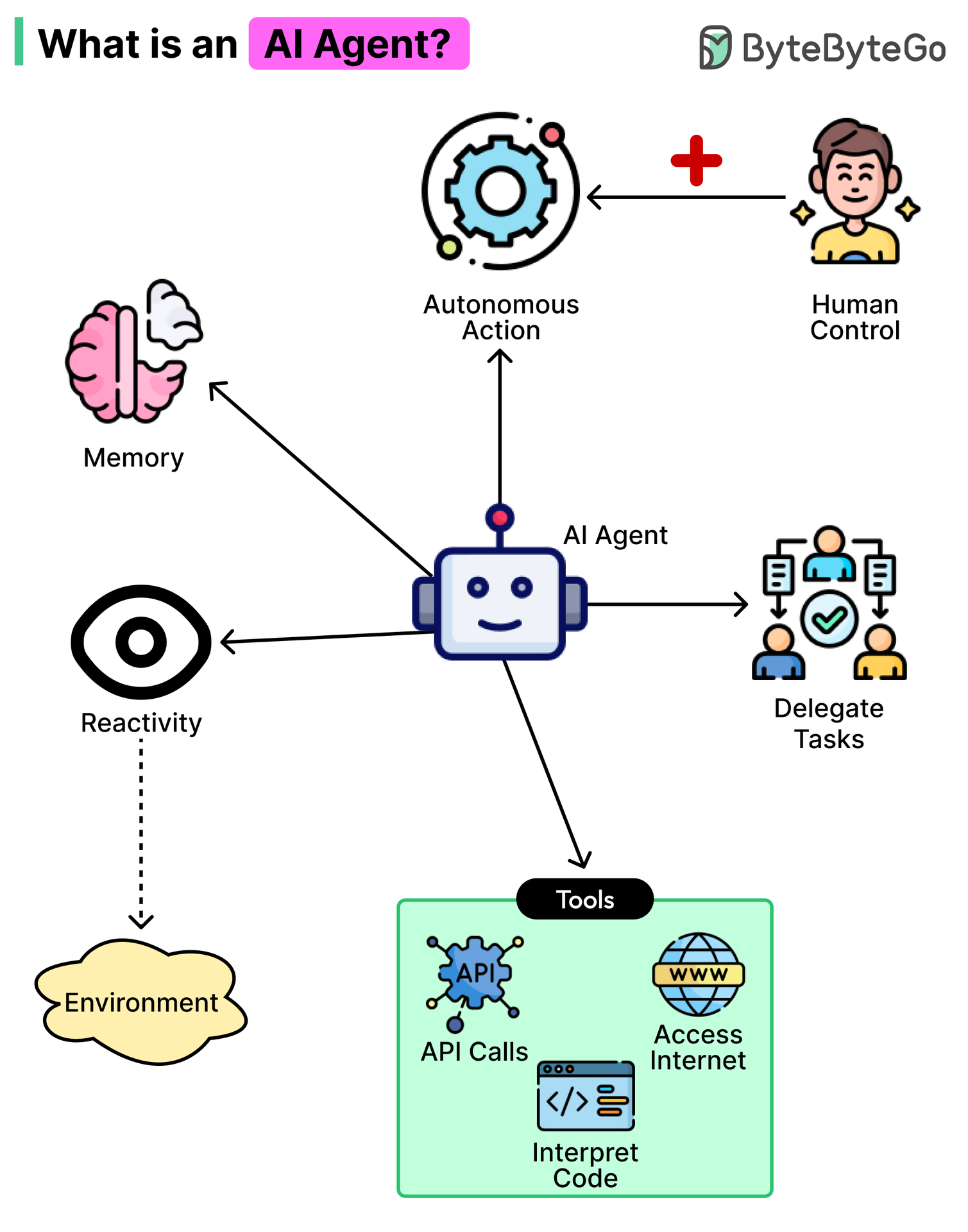
Agent has Autonomy ,planning, iteration, feedback, coordination( like if an Agent 1 do his work and now pass it to agent 4 to do next work) etc.
Information+action=Agent
Agentic ai has decision making and execution(via tools).
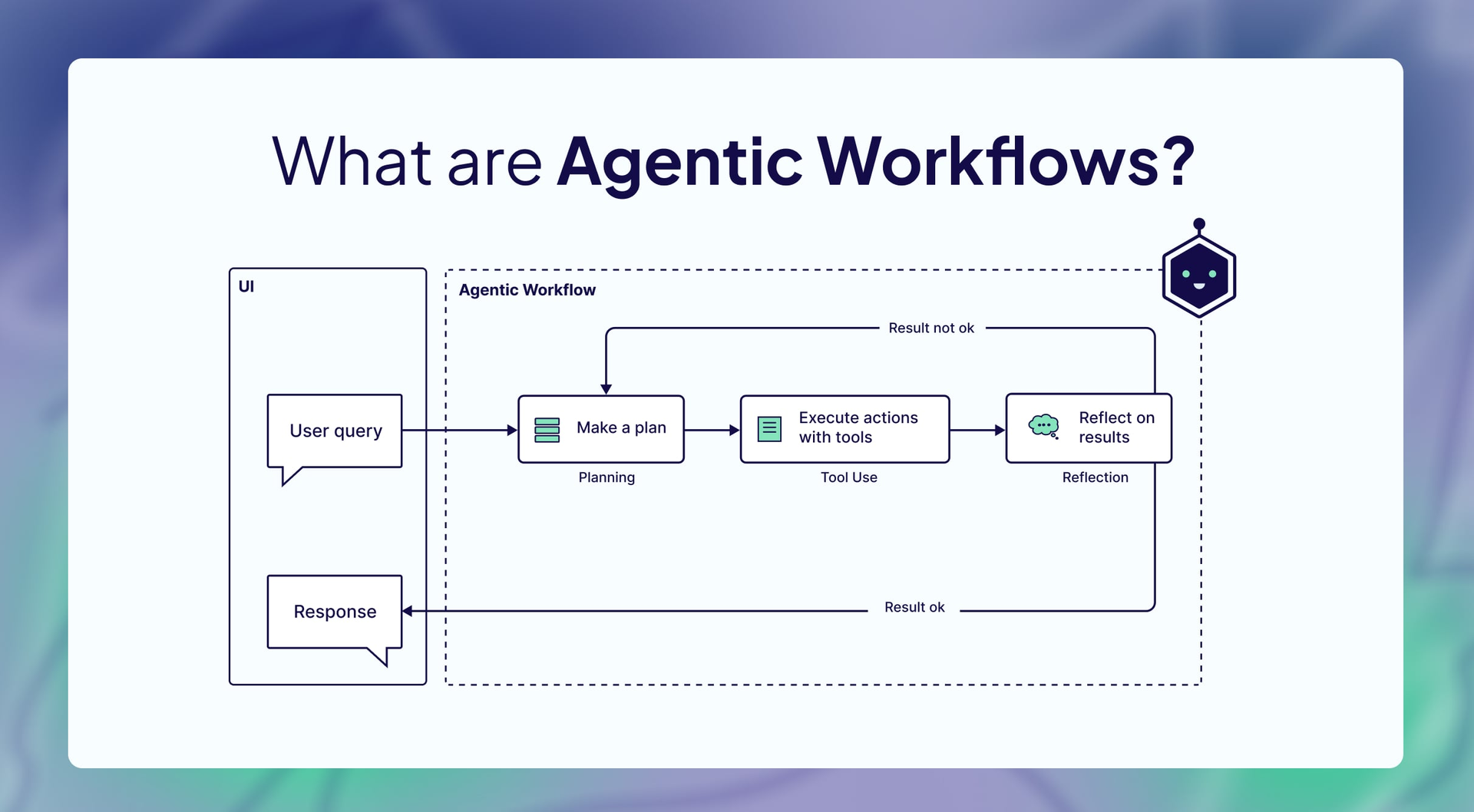
Agentic workflow
user send a query, it goes to planning agent(individual agent), the agent will have to use tool, execute action with tool, if result of action perform not ok, it will receive back to agent. if result ok the response to user. more there is possibilities there are more agents not single.
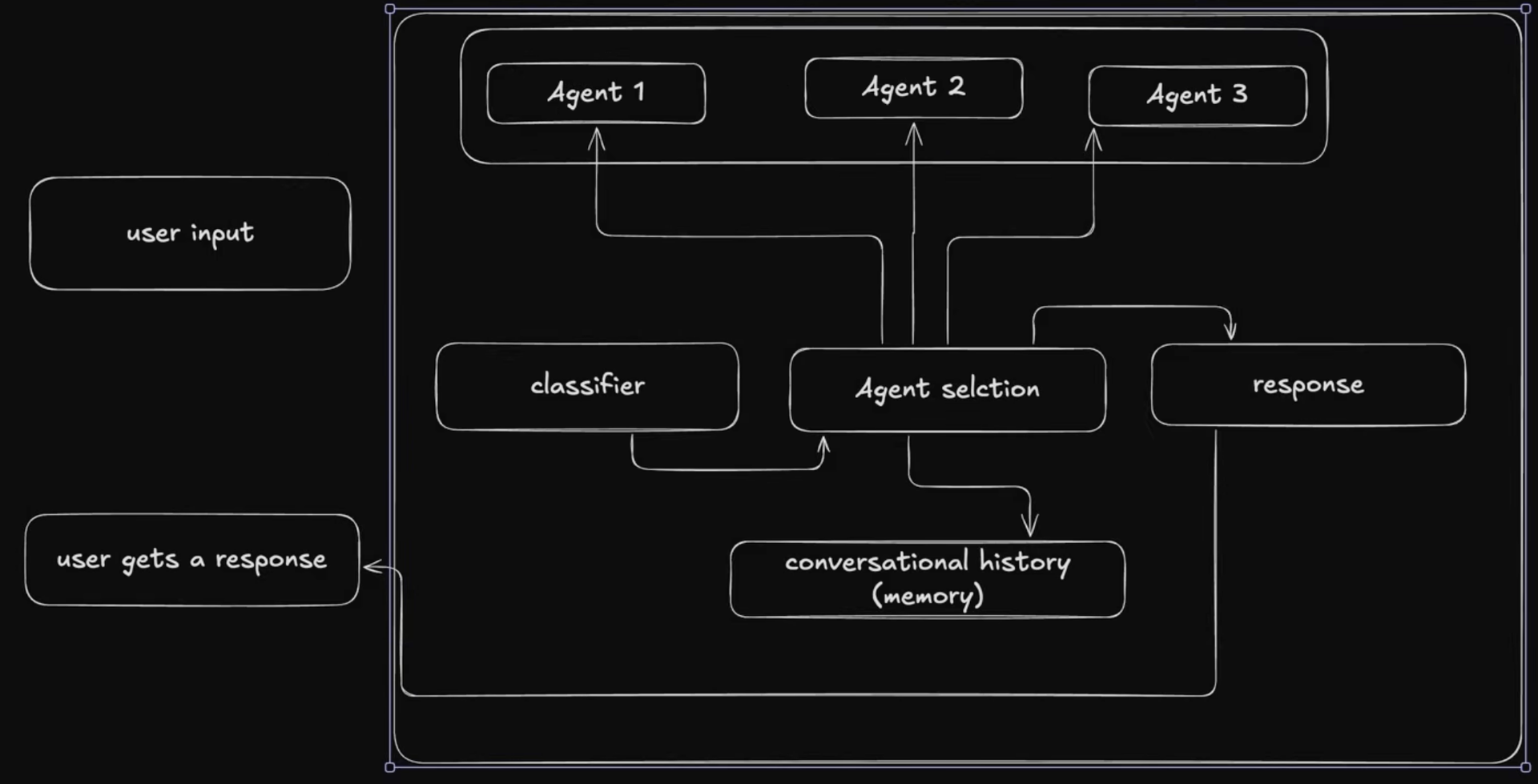
Multi agent workflow
Classifier tell the query is code generation or testcase or planning, we can ask LLM this. then we put agent selection tool. then agent selection which will run the agent workflow. the memory important because it track which agent you selected what was the response in last history so its like conversational history or memory.
AI as a Tool vs Agentic AI
🔹 Traditional AI (Tool Mode)
This is what most people use today:
You ask ChatGPT a question
It gives you an answer
You copy → paste → execute
You remain the decision-maker
It’s reactive.
You:
Ask for code
Fix errors manually
Decide next step
Deploy manually
AI = assistant
You = brain
Agentic AI (Agent-Based Systems)
Agentic AI = AI that:
Has a goal
Breaks it into tasks
Decides what to do next
Uses tools autonomously
Remembers context
Iterates until task is complete
AI = junior engineer + planner + executor
You = architect / supervisor
Agentic AI act autonoumsly, its combine reasoning ,memory and decision making.
It anlayzes, stratgies, act.
it reduce manual intervention, automate complex workflow.
Example : like self driving cars, autonoumous robots, AI assistants, AI power customer services.
Example below : AI assistant Planning your entire day, book meetings, handling emails without your constant input.
Agentic workflow
Text
What Does “From Tools to Thinking Systems” Mean?
A tool answers.
A thinking system:
Plans
Chooses actions
Evaluates results
Adjusts strategy
Continues autonomously
It behaves more like:
A developer
A DevOps engineer
A QA reviewer
A business analyst
Not just a chatbot.
Use Case in Your World (Odoo + DevOps + ERP)
Let’s use YOUR context.
🧠 Example 1: Odoo Feature Development Agent
Goal:
“Implement Saudi Mudad WPS integration in Odoo 17.”
Instead of:
You:
Ask ChatGPT
Write code
Debug
Deploy
Test manually
An Agentic System would:
Analyze module structure
Generate models + views
Run test suite
Fix errors automatically
Deploy to staging
Run post-deploy checks
Generate documentation
Open PR
Tag you for review
That’s not a tool.
That’s a system acting with intent.
AI Code Review Agent
You push code to GitHub.
Agent:
Reads diff
Detects anti-patterns
Checks Odoo ORM misuse
Flags performance issues
Checks security (sudo misuse, record rules)
Suggests improvements
Generates refactored version
It becomes your permanent reviewer.
Car Showroom AI Agent
Goal:
“Increase sales in Riyadh branch.”
Agent:
Analyzes stock
Checks slow-moving cars
Reviews pricing
Suggests discount campaigns
Creates WhatsApp campaign
Monitors responses
Adjusts strategy
That’s not GPT answering questions.
That’s AI acting strategically.
But There Is a Big Warning ⚠️
Agentic AI without:
Clear boundaries
Logging
Audit trails
Permission layers
Rollback mechanisms
= Disaster.
Especially in ERP.
Imagine an AI agent:
Deleting records
Posting wrong journal entries
Changing taxes
Deploying broken code
You must treat agents like junior engineers with limited access.
Claude Code behaves like an AI agent.
But it’s a controlled, scoped engineering agent, not a fully autonomous system.
Goal → Plan → Execute → Observe → Fix → Repeat
If a system does this without you manually copying & pasting each step → it’s agentic.
So technically:
Claude Code = Engineering Agent (within IDE context)
It doesn’t:
Wake up at night and refactor your ERP
Monitor production metrics
Auto-deploy without instruction
Strategize business improvements
It executes when told.
That makes it a:
🟢 “Supervised execution agent”
Not
🔴 “Autonomous strategic agent”